In the pursuit of energy efficiency, the choice of materials plays a crucial role, particularly when it comes to construction and architectural design. Insulated Aluminum Profiles have emerged as a top choice for energy-efficient building solutions due to their impressive thermal performance and durability. As industry expert Dr. Emily Thornton, a renowned energy efficiency consultant, states, "The integration of Insulated Aluminum Profiles in building design not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to a sustainable future." Her insights highlight the significant impact of these profiles on reducing energy consumption while maintaining structural integrity.
Selecting the right Insulated Aluminum Profiles involves understanding the various factors that influence their performance, including insulation thickness, thermal break technology, and overall design. As the demand for energy-efficient buildings continues to rise, understanding these elements is essential for architects, builders, and homeowners alike. The following sections will delve into key considerations to keep in mind when choosing Insulated Aluminum Profiles, ensuring that the selected materials meet the highest standards of energy efficiency and long-term sustainability.

Insulated aluminum profiles are integral components in modern construction, designed to enhance energy efficiency while maintaining structural integrity. These profiles are typically made by combining aluminum with thermal breaks, materials that prevent the transfer of heat. This construction technique is crucial in minimizing energy loss, creating a more comfortable indoor environment and reducing the demand for heating and cooling systems. As a result, buildings utilizing insulated aluminum profiles can achieve significant energy savings, both in operational costs and in reducing their carbon footprint.
The benefits of insulated aluminum profiles extend beyond energy efficiency. They offer exceptional durability and resistance to weathering, making them suitable for various climates. Furthermore, their lightweight nature allows for easier handling and installation, while their aesthetic versatility can meet diverse architectural styles. Additionally, these profiles often require less maintenance than traditional materials, ensuring long-term performance without the need for extensive upkeep. In summary, choosing insulated aluminum profiles can lead to substantial financial and environmental advantages, aligning with the modern focus on sustainable building practices.
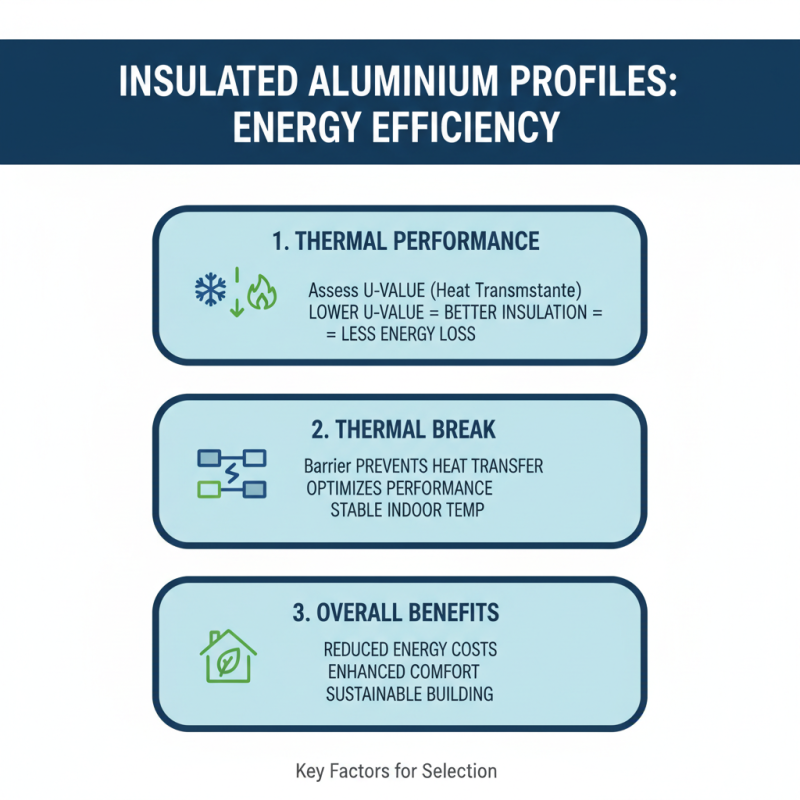
When selecting insulated aluminum profiles for energy efficiency, several key factors come into play. Firstly, the thermal performance of the profiles should be assessed, which involves looking at the thermal transmittance, or U-value. Lower U-values indicate better insulation properties, which can significantly reduce energy loss and enhance the overall energy efficiency of a building. Additionally, a profile that incorporates a thermal break—a barrier that prevents heat transfer—can further optimize thermal performance and help maintain a stable indoor environment.
Another important consideration is the design flexibility of the aluminum profiles. Profiles that can accommodate various insulation materials and thicknesses allow for custom solutions that align with specific energy efficiency goals. It’s essential to evaluate the compatibility of these profiles with other building materials to ensure a comprehensive approach to energy efficiency. Finally, local climate conditions must be taken into account during the selection process. In regions with extreme temperatures, choosing profiles designed for high thermal resistance will be crucial for achieving maximum energy efficiency and comfort.
When selecting insulated aluminum profiles for energy efficiency, it's essential to understand the various options available on the market. One common choice is the polyamide thermal break profiles, which utilize a polymer layer to substantially reduce thermal transfer between the exterior and interior. This type boasts impressive insulation properties, making it ideal for industrial and commercial applications where energy savings are a priority. They not only help in maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures but also contribute to reduced heating and cooling costs over time.
Another option worth considering is the structural thermal break profiles, which feature an advanced design that allows for enhanced structural strength while still providing thermal insulation. These profiles are built with materials that are engineered to minimize heat loss, making them suitable for residential uses as well. Moreover, they offer flexibility in design, allowing architects and builders to optimize both aesthetics and functionality. When comparing these types, evaluating performance metrics such as thermal transmittance (U-value) and the specific application environment can help in making an informed decision. This holistic approach ensures that the chosen profiles meet energy efficiency goals while satisfying design demands.
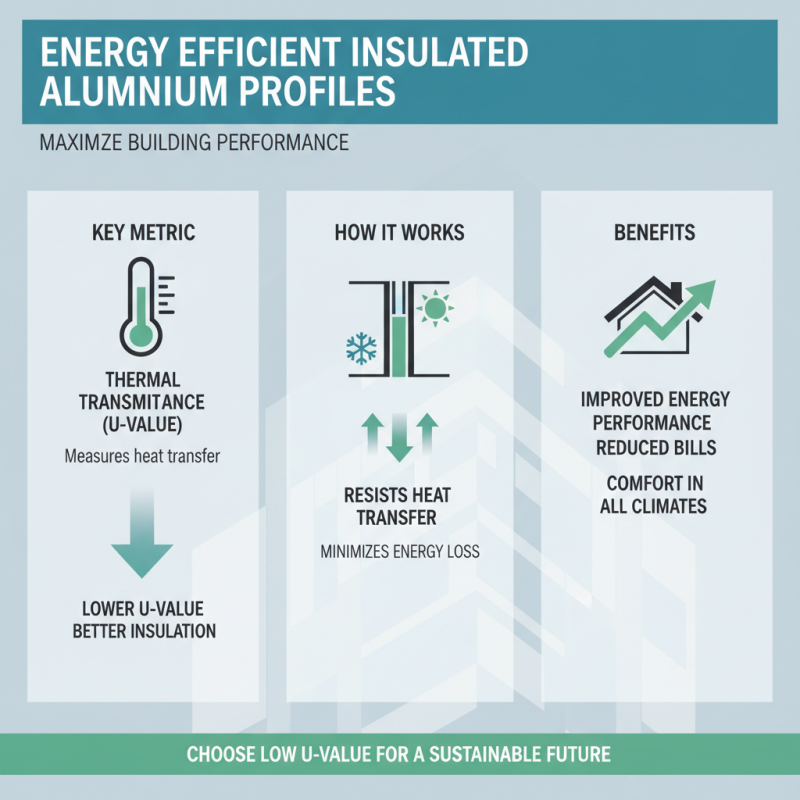
When selecting insulated aluminum profiles for energy efficiency, evaluating performance metrics is crucial. The thermal transmittance, or U-value, is one of the primary indicators. This metric measures how well the profile resists heat transfer; lower U-values signify better insulation. By choosing profiles with lower U-values, one can minimize energy loss and improve the overall energy performance of buildings, especially in extreme weather conditions.
Another important performance metric to consider is the Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC), which assesses how much solar radiation passes through the window or profile. A lower SHGC value indicates that less heat is gained from sunlight, thus reducing the need for cooling in warmer months. Additionally, consider the air leakage rating of the profiles. This metric evaluates how much air can pass through the frame and seals, with lower leakage rates leading to better insulation and enhanced energy efficiency. By carefully analyzing these performance metrics, one can make well-informed choices that contribute significantly to energy conservation and cost savings in the long run.
When considering insulation performance for aluminum profiles, proper installation is crucial to achieving optimal energy efficiency. One significant factor is the selection of appropriate spacers and seals that prevent thermal bridging, which can significantly compromise insulation properties. Using high-quality, flexible seals helps maintain the integrity of the thermal break, ensuring that the insulated aluminum profiles perform as intended in various weather conditions. This attention to detail during installation can significantly influence the overall energy efficiency of the building.
Another vital consideration is ensuring that the installation process is conducted in an environment free from contaminants such as dust and moisture, which can affect the adhesion of insulation components. Professionals should ensure that surfaces are clean and dry before installation, and they must use precise techniques to align profiles accurately. Additionally, employing thermal imaging technology post-installation can help identify any potential leaks or weak spots in insulation, allowing for timely adjustments that enhance the building's energy efficiency. Therefore, focusing on meticulous installation practices will play a pivotal role in leveraging the benefits of insulated aluminum profiles.
| Insulated Aluminum Profile Type | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Frame Depth (mm) | R-Value (m²K/W) | Air Leakage Rate (m³/h·m²) | Cost per Meter ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Thermal Profile | 1.8 | 70 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 20 |
| High-Performance Profile | 1.4 | 80 | 3.0 | 0.3 | 30 |
| Super Insulated Profile | 1.2 | 90 | 4.0 | 0.2 | 45 |
| Eco-Friendly Profile | 1.5 | 75 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 25 |